By calling this number, you consent to receive a follow-up text message from Erosion Control Direct if the call is missed
By calling this number, you consent to receive a follow-up text message from Erosion Control Direct if the call is missed
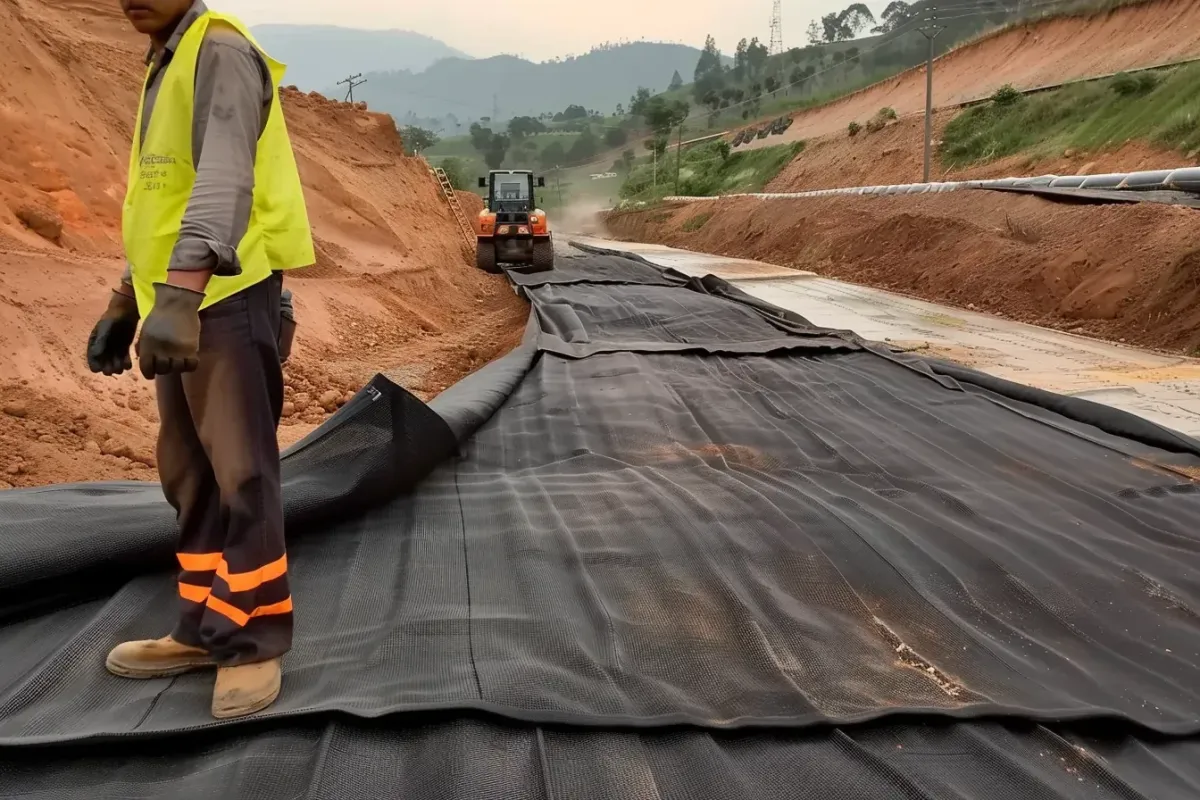
High-Quality Erosion Control Products for Every Project
Erosion Control Direct, Your Partner in Erosion Control Solutions
High-Quality Erosion Control Products for Every Project
Erosion Control Direct, Your Partner in Erosion Control Solutions
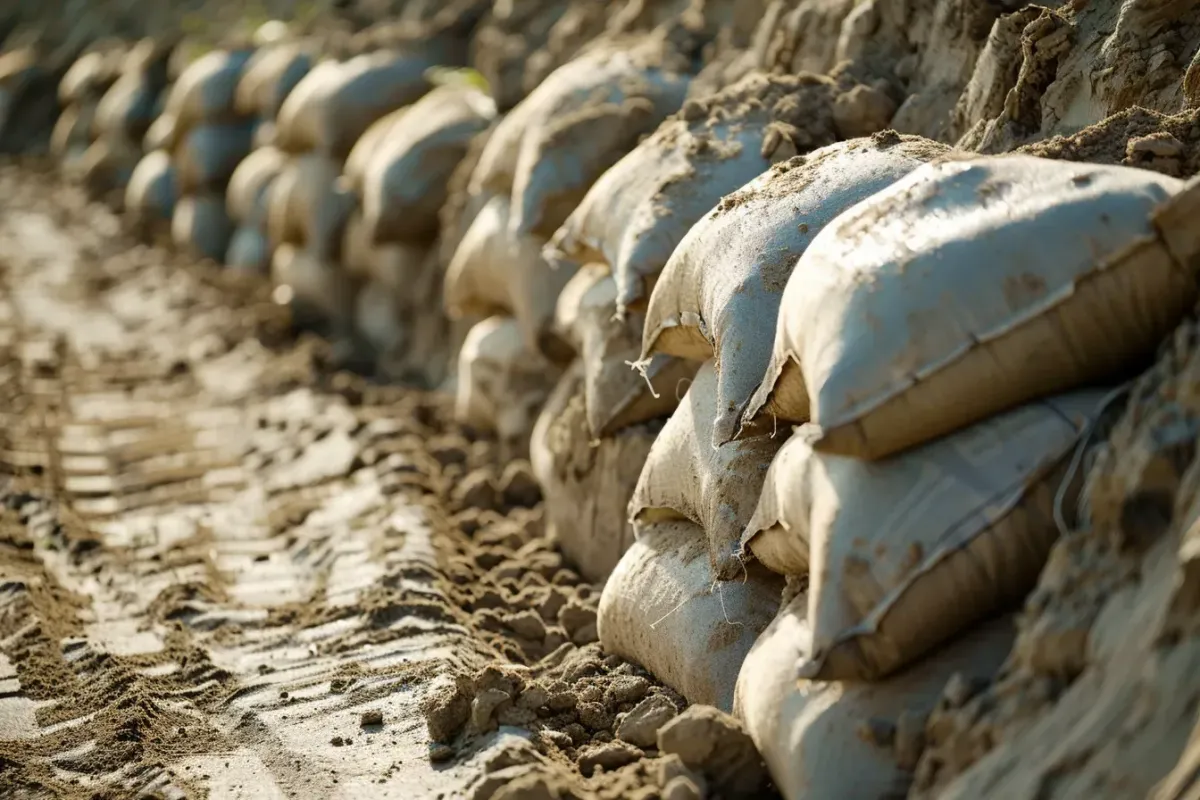
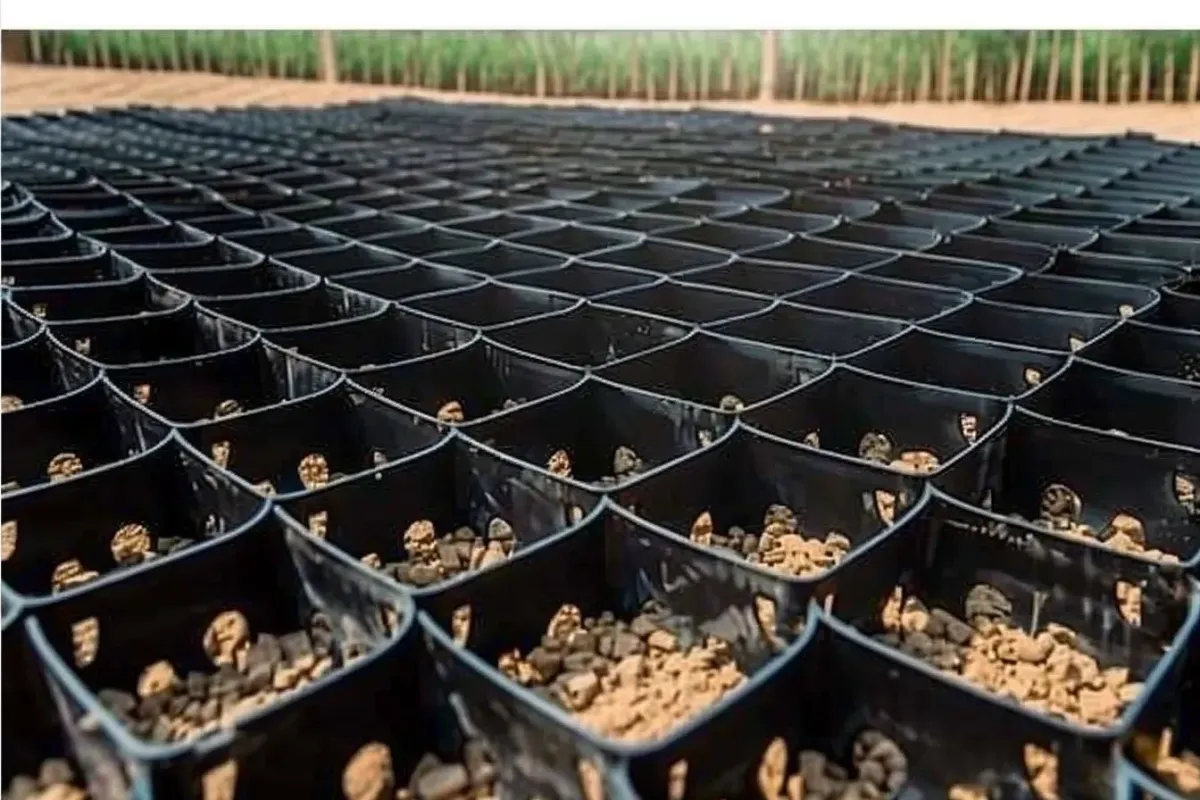
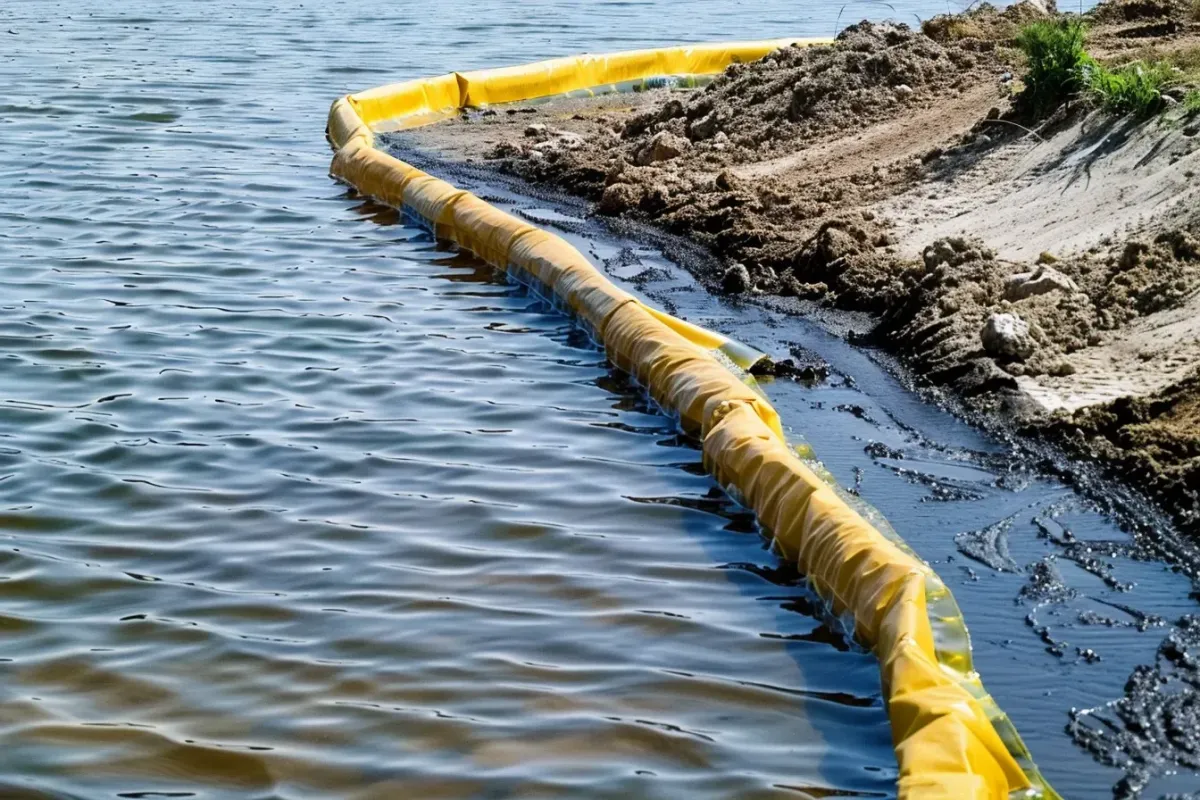
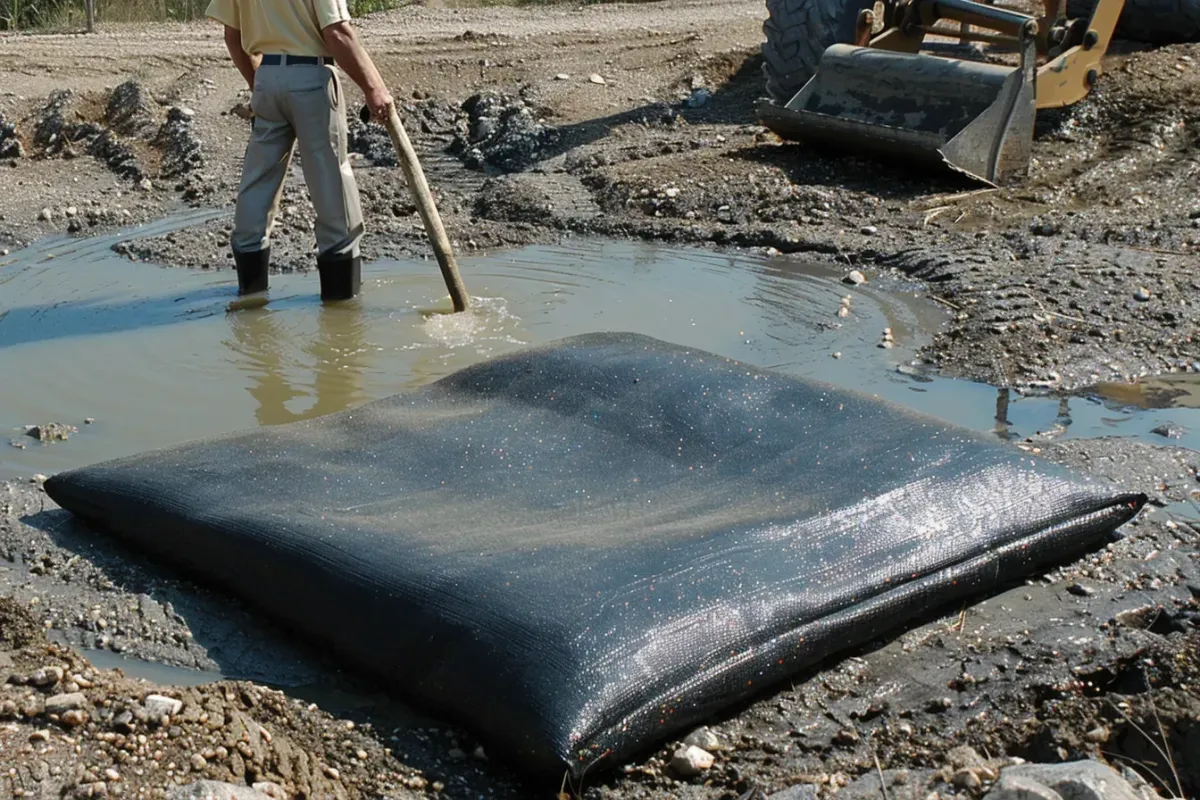
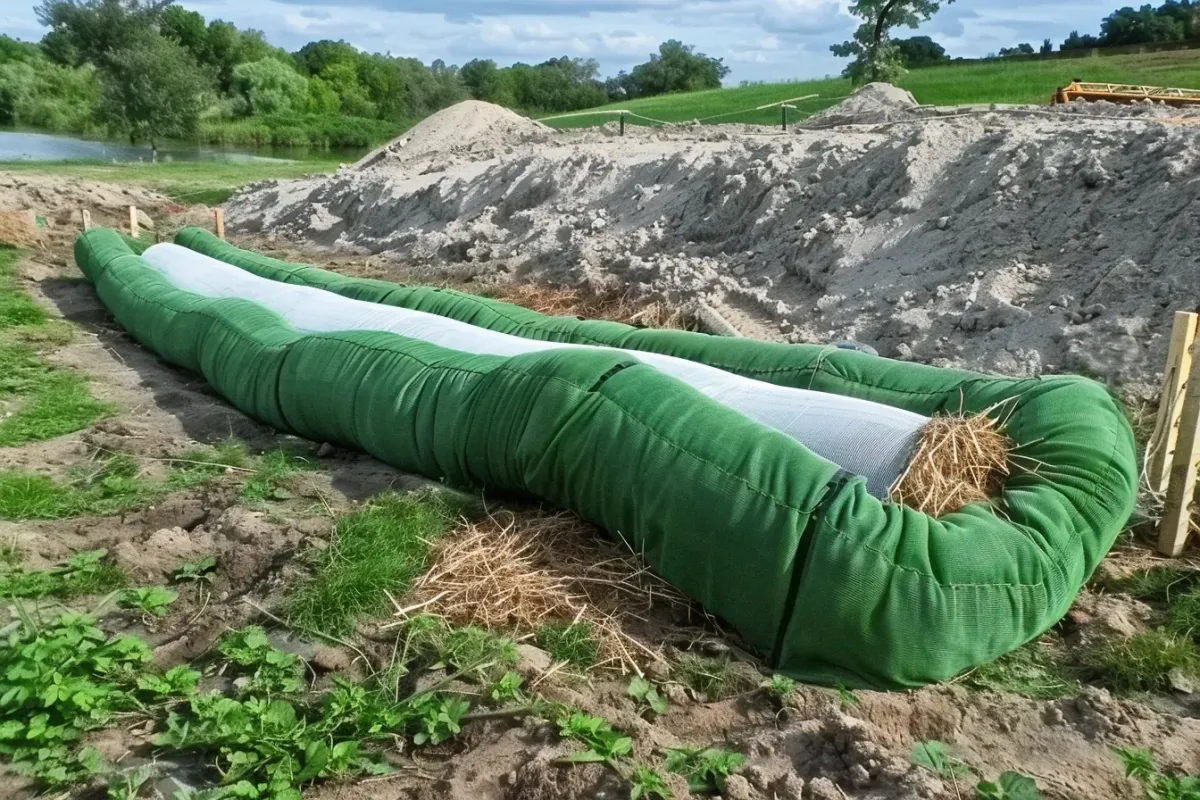
Our Erosion Control Products
Discover a Diverse Selection of Specialized Erosion Control Solutions Tailored to Safeguard Your Land
Our Erosion Control Products
Discover a Diverse Selection of Specialized Erosion Control Solutions Tailored to Safeguard Your Land
Need a Quotation?
Click below to speak with one of our professionals
Need a Quotation?
Click below to speak with one of our professionals
Why Choose Erosion Control Direct?
Choosing Erosion Control Direct for your erosion control needs means partnering with a seasoned expert in the field. With over a decade of experience, we have honed our expertise in supplying top-quality erosion control products. Our comprehensive range of solutions, from silt fences to geotextile fabrics, is designed to meet the diverse needs of both large-scale construction projects and small-scale landscaping efforts.
Our commitment to quality and sustainability ensures that every product in our inventory not only meets but exceeds industry standards. We understand the critical importance of protecting the environment while maintaining project timelines and budgets. That's why we offer products that are both effective and eco-friendly, providing you with the tools you need to prevent soil erosion, stabilize terrain, and promote healthy vegetation growth.
At Erosion Control Direct, we believe in building strong relationships with our clients in the United States. Our knowledgeable team is always on hand to provide expert advice, ensuring you select the right products for your specific erosion control challenges. With our proven track record, dedication to customer service, and unwavering commitment to environmental stewardship, Erosion Control Direct is your trusted partner in safeguarding your landscapes and construction sites against erosion.
Why Choose Erosion Control Direct?
Choosing Erosion Control Direct for your erosion control needs means partnering with a seasoned expert in the field. With over a decade of experience, we have honed our expertise in supplying top-quality erosion control products. Our comprehensive range of solutions, from silt fences to geotextile fabrics, is designed to meet the diverse needs of both large-scale construction projects and small-scale landscaping efforts.
Our commitment to quality and sustainability ensures that every product in our inventory not only meets but exceeds industry standards. We understand the critical importance of protecting the environment while maintaining project timelines and budgets. That's why we offer products that are both effective and eco-friendly, providing you with the tools you need to prevent soil erosion, stabilize terrain, and promote healthy vegetation growth.
At Erosion Control Direct, we believe in building strong relationships with our clients in the United States. Our knowledgeable team is always on hand to provide expert advice, ensuring you select the right products for your specific erosion control challenges. With our proven track record, dedication to customer service, and unwavering commitment to environmental stewardship, Erosion Control Direct is your trusted partner in safeguarding your landscapes and construction sites against erosion.
Featured Blog Articles
From the Experts: Navigating the Landscape of Erosion Control

Understanding Erosion Control Costs: A Comprehensive Breakdown for Project Planning
Erosion control is a vital aspect of environmental conservation and sustainable land management. It involves implementing measures to prevent soil erosion, protect water quality, and maintain the stability of landscapes. However, one of the most critical considerations for any erosion control project is cost. Understanding the various factors that influence erosion control costs can help project managers, landowners, and policymakers make informed decisions and optimize their budgets.
When planning an erosion control project, having access to high-quality erosion control products is essential. These products form the foundation of any successful erosion management strategy, helping to prevent soil loss, protect water quality, and maintain site stability.
Factors Influencing Erosion Control Costs
Several factors can influence the cost of erosion control measures. These include:
1. Project Size and Scope
The size and scope of the project are primary determinants of cost. Larger projects typically require more materials, labor, and time, leading to higher overall expenses.
2. Site Conditions
Site-specific conditions, such as soil type, slope gradient, and vegetation cover, can significantly impact the cost of erosion control. For example, steep slopes may require more intensive stabilization measures, while sandy soils may need additional reinforcement.
3. Type of Erosion Control Methods
Different erosion control methods come with varying costs. Common methods include:
Vegetative Solutions: Planting grass, shrubs, or trees to stabilize soil. This method is generally cost-effective but may require ongoing maintenance.
Structural Solutions: Building retaining walls, terraces, or riprap. These methods are more expensive due to material and labor costs but offer long-term stability.
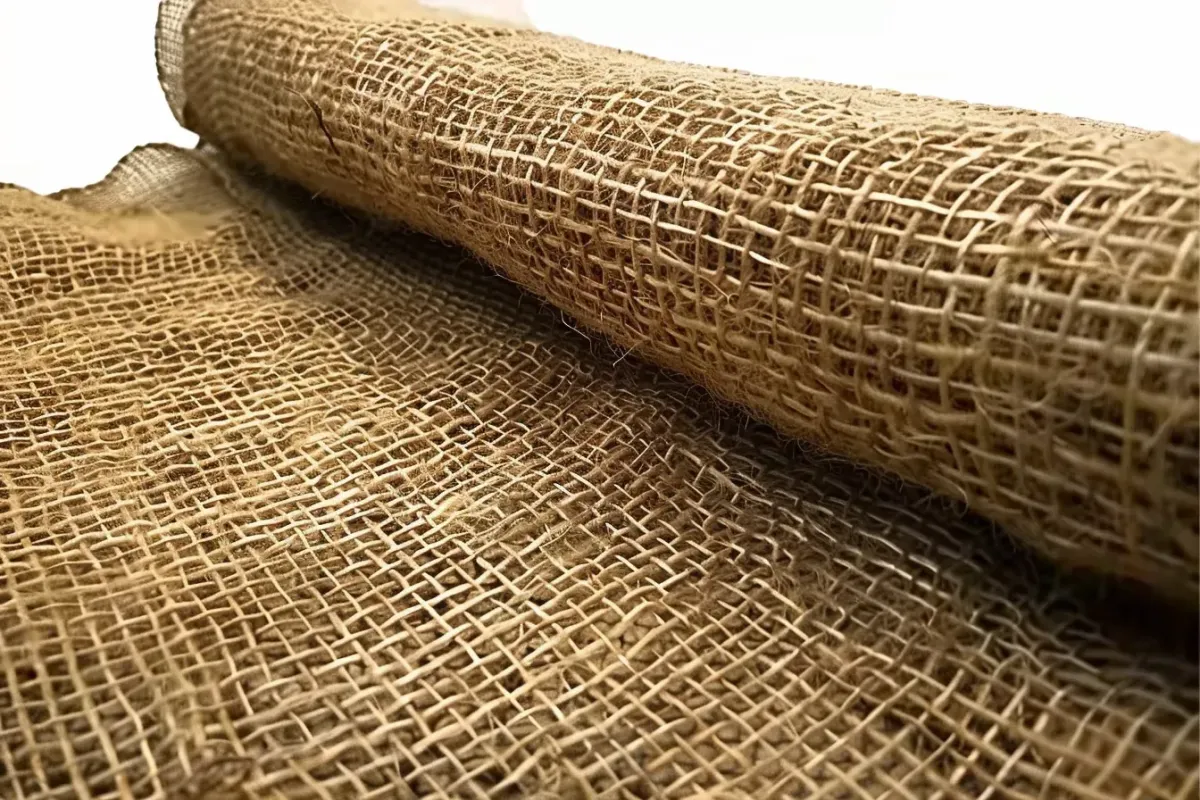
Erosion Control Blankets and Mats: Using biodegradable or synthetic mats to protect soil. These products vary in cost depending on the material and coverage area.
4. Labor and Installation
Labor costs can vary based on the complexity of the project and the expertise required. Installation costs also depend on the type of erosion control measures being implemented and the site’s accessibility.
5. Maintenance and Monitoring
Ongoing maintenance and monitoring are essential for the long-term success of erosion control measures. These costs should be factored into the overall budget.
6. Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with local, state, and federal regulations can also influence costs. Projects may require permits, inspections, and adherence to specific guidelines, which can add to the overall expense.
Cost Breakdown of Common Erosion Control Methods
To provide a clearer understanding of erosion control costs, let’s examine some common methods and their associated expenses.
1. Vegetative Solutions
Vegetative solutions are often the most cost-effective option for erosion control. These methods include:
Grass Seeding: Costs range from $0.001 to $0.02 per square foot, depending on the type of grass and site preparation required.
Shrub and Tree Planting: Costs vary based on the species and size of the plants. On average, planting shrubs and trees can range from $1 to $5 per square foot.
2. Structural Solutions
Structural solutions provide long-term stability but are generally more expensive. Common methods include:
Retaining Walls: Costs range from $20 to $40 per square foot, depending on the materials used (e.g., concrete, stone, timber) and the complexity of the installation.
Terracing: Costs vary based on the slope gradient and the materials used. On average, terracing can range from $10 to $30 per square foot.
Riprap: Costs range from $35 to $50 per linear foot, depending on the size and type of rock used.
3. Erosion Control Blankets and Mats
Erosion control blankets and mats are used to protect soil from erosion while vegetation establishes. Costs vary based on the material and coverage area:
Biodegradable Blankets: Made from materials like straw, coconut fiber, or jute, these blankets cost between $0.50 and $1.50 per square foot.
Synthetic Mats: Made from materials like polypropylene, these mats cost between $1 and $3 per square foot.
4. Silt Fences and Sediment Barriers
Silt fences and sediment barriers are used to control sediment runoff from construction sites and other disturbed areas. Costs include:
Silt Fences: Costs range from $0.75 to $1.50 per linear foot, depending on the height and material used.
Sediment Barriers: Costs vary based on the type of barrier (e.g., compost filter socks, straw bales) and the coverage area. On average, sediment barriers can range from $2 to $5 per linear foot.
Case Study: Erosion Control Costs for Highway Projects
A study conducted by the International Erosion Control Association (IECA) examined the costs of erosion and sediment control (ESC) for highway projects across the United States. The study found that ESC costs as a function of total highway construction project costs averaged 3%. The study also provided detailed cost data for various ESC methods, including riprap, seeding and mulching, erosion control mats, silt fences, sodding, and hard armor.
Key Findings from the Study
Average Annual ESC Expenditures: The average annual ESC expenditure for state highway projects was $9.01 million.
Cost Per State Land Area: The average cost per state land area was $252.6 per square mile, with the highest expenditure reported in New Mexico at $1,493 per square mile.
Cost Per Capita: The average cost per capita was $2.20, with Wyoming reporting the highest expenditure at $10.1 per person.
These findings highlight the significant investment required for effective erosion and sediment control in large-scale infrastructure projects.
Strategies for Reducing Erosion Control Costs
Reducing the cost of erosion control initiatives involves strategic planning, the adoption of sustainable practices, and the implementation of erosion prevention measures. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Conduct Thorough Site Assessments
A thorough assessment of the site’s topography, soil type, and environmental conditions is essential for developing an effective erosion control plan. By understanding the natural processes at play, project managers can tailor their erosion control measures to the specific needs of the site, eliminating unnecessary expenses associated with ineffective solutions.
2. Implement Sustainable Practices
Incorporating sustainable methods in erosion control initiatives can reduce ongoing maintenance costs and benefit the surrounding ecosystem. Bioengineering solutions, such as vegetative covers or natural structures, provide long-term erosion protection at a lower cost compared to traditional hard engineering approaches.
3. Optimize Planning and Design
Effective erosion control cost reduction begins with meticulous planning and design. Incorporating suitable erosion control products and adhering to industry standards can optimize project outcomes and minimize costs.
4. Use Cost-Effective Materials
Selecting cost-effective materials that offer durability and environmental benefits can help reduce overall expenses. For example, using biodegradable erosion control blankets or compost filter socks can provide effective erosion control while minimizing waste and disposal costs.
5. Leverage Technology
Utilizing advanced technologies, such as remote sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS), can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of erosion control efforts. These tools allow for precise mapping of erosion-prone areas, monitoring of site conditions, and targeted implementation of erosion control measures.
Expert Perspectives on Erosion Control Costs
To gain further insight into the costs associated with erosion control, we reached out to industry experts:
Dr. David R. Montgomery, a geomorphologist at the University of Washington, emphasizes the importance of investing in erosion control:
“Investing in erosion control is not just about preventing soil loss; it’s about protecting our water quality, infrastructure, and ecosystems. While the upfront costs may seem significant, the long-term benefits far outweigh the expenses. Effective erosion control measures can save millions in repair and maintenance costs down the line.”
Comparison of Erosion Control Costs
Conclusion
Understanding the costs associated with erosion control is crucial for effective project planning and budget optimization. By considering factors such as project size, site conditions, and the type of erosion control methods, project managers can develop comprehensive and cost-effective erosion control strategies.
As we continue to advance in the field of erosion control, it’s essential to stay informed about the latest developments and best practices. For instance, understanding the costs and benefits of different erosion control methods can help land managers make informed decisions about the most suitable approaches for their specific situations. Additionally, considering the broader context of forest erosion control and wetland erosion control can provide valuable insights into the most effective strategies for preserving our natural resources.
Q&A
Q: What factors influence the cost of erosion control?
A: The cost of erosion control is influenced by factors such as project size, site conditions, type of erosion control methods, labor and installation costs, maintenance and monitoring requirements, and regulatory compliance.
Q: What are some cost-effective erosion control methods?
A: Cost-effective erosion control methods include vegetative solutions like grass seeding and shrub planting, as well as using biodegradable erosion control blankets and compost filter socks.
Q: How can I reduce the cost of erosion control for my project?
A: To reduce the cost of erosion control, conduct thorough site assessments, implement sustainable practices, optimize planning and design, use cost-effective materials, and leverage advanced technologies like remote sensing and GIS.
Q: What are the benefits of investing in erosion control?
A: Investing in erosion control helps prevent soil loss, protect water quality, maintain infrastructure stability, and preserve ecosystems. It can also save money in the long run by reducing repair and maintenance costs.
Q: How do site conditions affect erosion control costs?
A: Site conditions such as soil type, slope gradient, and vegetation cover can impact the cost of erosion control. For example, steep slopes may require more intensive stabilization measures, while sandy soils may need additional reinforcement.
Q: What are the average costs of common erosion control methods?
A: Average costs vary by method. For example, grass seeding costs $0.001 to $0.02 per square foot, retaining walls cost $20 to $40 per square foot, and biodegradable erosion control blankets cost $0.50 to $1.50 per square foot.
Q: Are there any long-term cost benefits of erosion control?
A: Yes, long-term benefits include reduced maintenance and repair costs, improved land productivity, protection of infrastructure and property, and enhanced environmental sustainability.
Q: How do regulatory requirements impact erosion control costs?
A: Regulatory requirements can add to the overall cost of erosion control projects by necessitating permits, inspections, and adherence to specific guidelines. Compliance with these regulations is essential for project success.
Q: What role does technology play in reducing erosion control costs?
A: Technology, such as remote sensing and GIS, enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of erosion control efforts by allowing for precise mapping, monitoring, and targeted implementation of measures.
Q: Can erosion control be included in construction budgets?
A: Yes, erosion control can and should be included in construction budgets as a separate line item. Considering erosion control measures during the planning stage helps avoid unexpected costs during construction.
Get Expert Erosion Control Solutions
Implementing the right erosion control solutions is crucial for protecting your property and the environment. At Erosion Control Direct, we’re committed to providing you with top-quality products and expert advice to address your specific erosion control needs. For personalized assistance and product recommendations, don’t hesitate to reach out:
Call us at (888) 920-5005 to speak with one of our erosion control experts.
Visit our website at https://erosioncontroldirect.com to browse our product range or submit an online inquiry.
For detailed quotations, email us at [email protected].
Let us help you find the perfect erosion control solution for your project. Contact Erosion Control Direct today and take the first step towards effective soil stabilization and environmental protection.
Featured Blog Articles
From the Experts: Navigating the Landscape of Erosion Control

Understanding Erosion Control Costs: A Comprehensive Breakdown for Project Planning
Erosion control is a vital aspect of environmental conservation and sustainable land management. It involves implementing measures to prevent soil erosion, protect water quality, and maintain the stability of landscapes. However, one of the most critical considerations for any erosion control project is cost. Understanding the various factors that influence erosion control costs can help project managers, landowners, and policymakers make informed decisions and optimize their budgets.
When planning an erosion control project, having access to high-quality erosion control products is essential. These products form the foundation of any successful erosion management strategy, helping to prevent soil loss, protect water quality, and maintain site stability.
Factors Influencing Erosion Control Costs
Several factors can influence the cost of erosion control measures. These include:
1. Project Size and Scope
The size and scope of the project are primary determinants of cost. Larger projects typically require more materials, labor, and time, leading to higher overall expenses.
2. Site Conditions
Site-specific conditions, such as soil type, slope gradient, and vegetation cover, can significantly impact the cost of erosion control. For example, steep slopes may require more intensive stabilization measures, while sandy soils may need additional reinforcement.
3. Type of Erosion Control Methods
Different erosion control methods come with varying costs. Common methods include:
Vegetative Solutions: Planting grass, shrubs, or trees to stabilize soil. This method is generally cost-effective but may require ongoing maintenance.
Structural Solutions: Building retaining walls, terraces, or riprap. These methods are more expensive due to material and labor costs but offer long-term stability.
Erosion Control Blankets and Mats: Using biodegradable or synthetic mats to protect soil. These products vary in cost depending on the material and coverage area.
4. Labor and Installation
Labor costs can vary based on the complexity of the project and the expertise required. Installation costs also depend on the type of erosion control measures being implemented and the site’s accessibility.
5. Maintenance and Monitoring
Ongoing maintenance and monitoring are essential for the long-term success of erosion control measures. These costs should be factored into the overall budget.
6. Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with local, state, and federal regulations can also influence costs. Projects may require permits, inspections, and adherence to specific guidelines, which can add to the overall expense.
Cost Breakdown of Common Erosion Control Methods
To provide a clearer understanding of erosion control costs, let’s examine some common methods and their associated expenses.
1. Vegetative Solutions
Vegetative solutions are often the most cost-effective option for erosion control. These methods include:
Grass Seeding: Costs range from $0.001 to $0.02 per square foot, depending on the type of grass and site preparation required.
Shrub and Tree Planting: Costs vary based on the species and size of the plants. On average, planting shrubs and trees can range from $1 to $5 per square foot.
2. Structural Solutions
Structural solutions provide long-term stability but are generally more expensive. Common methods include:
Retaining Walls: Costs range from $20 to $40 per square foot, depending on the materials used (e.g., concrete, stone, timber) and the complexity of the installation.
Terracing: Costs vary based on the slope gradient and the materials used. On average, terracing can range from $10 to $30 per square foot.
Riprap: Costs range from $35 to $50 per linear foot, depending on the size and type of rock used.
3. Erosion Control Blankets and Mats
Erosion control blankets and mats are used to protect soil from erosion while vegetation establishes. Costs vary based on the material and coverage area:
Biodegradable Blankets: Made from materials like straw, coconut fiber, or jute, these blankets cost between $0.50 and $1.50 per square foot.
Synthetic Mats: Made from materials like polypropylene, these mats cost between $1 and $3 per square foot.
4. Silt Fences and Sediment Barriers
Silt fences and sediment barriers are used to control sediment runoff from construction sites and other disturbed areas. Costs include:
Silt Fences: Costs range from $0.75 to $1.50 per linear foot, depending on the height and material used.
Sediment Barriers: Costs vary based on the type of barrier (e.g., compost filter socks, straw bales) and the coverage area. On average, sediment barriers can range from $2 to $5 per linear foot.
Case Study: Erosion Control Costs for Highway Projects
A study conducted by the International Erosion Control Association (IECA) examined the costs of erosion and sediment control (ESC) for highway projects across the United States. The study found that ESC costs as a function of total highway construction project costs averaged 3%. The study also provided detailed cost data for various ESC methods, including riprap, seeding and mulching, erosion control mats, silt fences, sodding, and hard armor.
Key Findings from the Study
Average Annual ESC Expenditures: The average annual ESC expenditure for state highway projects was $9.01 million.
Cost Per State Land Area: The average cost per state land area was $252.6 per square mile, with the highest expenditure reported in New Mexico at $1,493 per square mile.
Cost Per Capita: The average cost per capita was $2.20, with Wyoming reporting the highest expenditure at $10.1 per person.
These findings highlight the significant investment required for effective erosion and sediment control in large-scale infrastructure projects.
Strategies for Reducing Erosion Control Costs
Reducing the cost of erosion control initiatives involves strategic planning, the adoption of sustainable practices, and the implementation of erosion prevention measures. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Conduct Thorough Site Assessments
A thorough assessment of the site’s topography, soil type, and environmental conditions is essential for developing an effective erosion control plan. By understanding the natural processes at play, project managers can tailor their erosion control measures to the specific needs of the site, eliminating unnecessary expenses associated with ineffective solutions.
2. Implement Sustainable Practices
Incorporating sustainable methods in erosion control initiatives can reduce ongoing maintenance costs and benefit the surrounding ecosystem. Bioengineering solutions, such as vegetative covers or natural structures, provide long-term erosion protection at a lower cost compared to traditional hard engineering approaches.
3. Optimize Planning and Design
Effective erosion control cost reduction begins with meticulous planning and design. Incorporating suitable erosion control products and adhering to industry standards can optimize project outcomes and minimize costs.
4. Use Cost-Effective Materials
Selecting cost-effective materials that offer durability and environmental benefits can help reduce overall expenses. For example, using biodegradable erosion control blankets or compost filter socks can provide effective erosion control while minimizing waste and disposal costs.
5. Leverage Technology
Utilizing advanced technologies, such as remote sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS), can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of erosion control efforts. These tools allow for precise mapping of erosion-prone areas, monitoring of site conditions, and targeted implementation of erosion control measures.
Expert Perspectives on Erosion Control Costs
To gain further insight into the costs associated with erosion control, we reached out to industry experts:
Dr. David R. Montgomery, a geomorphologist at the University of Washington, emphasizes the importance of investing in erosion control:
“Investing in erosion control is not just about preventing soil loss; it’s about protecting our water quality, infrastructure, and ecosystems. While the upfront costs may seem significant, the long-term benefits far outweigh the expenses. Effective erosion control measures can save millions in repair and maintenance costs down the line.”
Comparison of Erosion Control Costs
Conclusion
Understanding the costs associated with erosion control is crucial for effective project planning and budget optimization. By considering factors such as project size, site conditions, and the type of erosion control methods, project managers can develop comprehensive and cost-effective erosion control strategies.
As we continue to advance in the field of erosion control, it’s essential to stay informed about the latest developments and best practices. For instance, understanding the costs and benefits of different erosion control methods can help land managers make informed decisions about the most suitable approaches for their specific situations. Additionally, considering the broader context of forest erosion control and wetland erosion control can provide valuable insights into the most effective strategies for preserving our natural resources.
Q&A
Q: What factors influence the cost of erosion control?
A: The cost of erosion control is influenced by factors such as project size, site conditions, type of erosion control methods, labor and installation costs, maintenance and monitoring requirements, and regulatory compliance.
Q: What are some cost-effective erosion control methods?
A: Cost-effective erosion control methods include vegetative solutions like grass seeding and shrub planting, as well as using biodegradable erosion control blankets and compost filter socks.
Q: How can I reduce the cost of erosion control for my project?
A: To reduce the cost of erosion control, conduct thorough site assessments, implement sustainable practices, optimize planning and design, use cost-effective materials, and leverage advanced technologies like remote sensing and GIS.
Q: What are the benefits of investing in erosion control?
A: Investing in erosion control helps prevent soil loss, protect water quality, maintain infrastructure stability, and preserve ecosystems. It can also save money in the long run by reducing repair and maintenance costs.
Q: How do site conditions affect erosion control costs?
A: Site conditions such as soil type, slope gradient, and vegetation cover can impact the cost of erosion control. For example, steep slopes may require more intensive stabilization measures, while sandy soils may need additional reinforcement.
Q: What are the average costs of common erosion control methods?
A: Average costs vary by method. For example, grass seeding costs $0.001 to $0.02 per square foot, retaining walls cost $20 to $40 per square foot, and biodegradable erosion control blankets cost $0.50 to $1.50 per square foot.
Q: Are there any long-term cost benefits of erosion control?
A: Yes, long-term benefits include reduced maintenance and repair costs, improved land productivity, protection of infrastructure and property, and enhanced environmental sustainability.
Q: How do regulatory requirements impact erosion control costs?
A: Regulatory requirements can add to the overall cost of erosion control projects by necessitating permits, inspections, and adherence to specific guidelines. Compliance with these regulations is essential for project success.
Q: What role does technology play in reducing erosion control costs?
A: Technology, such as remote sensing and GIS, enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of erosion control efforts by allowing for precise mapping, monitoring, and targeted implementation of measures.
Q: Can erosion control be included in construction budgets?
A: Yes, erosion control can and should be included in construction budgets as a separate line item. Considering erosion control measures during the planning stage helps avoid unexpected costs during construction.
Get Expert Erosion Control Solutions
Implementing the right erosion control solutions is crucial for protecting your property and the environment. At Erosion Control Direct, we’re committed to providing you with top-quality products and expert advice to address your specific erosion control needs. For personalized assistance and product recommendations, don’t hesitate to reach out:
Call us at (888) 920-5005 to speak with one of our erosion control experts.
Visit our website at https://erosioncontroldirect.com to browse our product range or submit an online inquiry.
For detailed quotations, email us at [email protected].
Let us help you find the perfect erosion control solution for your project. Contact Erosion Control Direct today and take the first step towards effective soil stabilization and environmental protection.
FAQs
Your frequently asked questions answered
What is the best material to stop erosion?
The best material to stop erosion can vary depending on the specific conditions and requirements of the site in question. Organic mulches like straw and wood fiber are indeed very effective, as they not only shield the soil from the direct impact of rainfall but also facilitate the establishment of vegetation by improving soil moisture retention. For steeper slopes or areas with faster-moving water, erosion control blankets, coir logs (coconut husk), or riprap—large stones used to stabilize shorelines and stream banks—may be necessary. In addition, living plants are excellent at preventing erosion; deep-rooted grasses and shrubs can stabilize the soil and dissipate the energy of flowing water. Ultimately, the optimal choice is a combination of materials and methods tailored to the local environment, soil type, slope, and the level of erosive forces present.
What is the best erosion control?
The best erosion control strategies typically involve a combination of techniques that address the specific needs of the landscape in question. These strategies can include the use of physical barriers such as rocks, sediment control logs, and perimeter control fencing to intercept and slow down surface water flow, thereby reducing erosion potential. Vegetative measures are also pivotal, with plants, grasses, and trees acting as a natural defense to anchor the soil. Moreover, land management practices like terracing and contouring can significantly decrease erosion on slopes by altering the physical landscape to minimize runoff velocity and soil displacement. Selecting and combining these approaches based on the land's characteristics ensures the most effective protection against erosion.
What is the cheapest erosion control?
The cheapest erosion control methods are those that are cost-effective and make use of readily available materials. These often include the application of agricultural by-products such as straw, which can be used as a mulch to cover bare soil and prevent erosion. Planting fast-growing grasses or ground cover is another economical solution, as it provides quick stabilization of the soil with the additional benefit of enhancing the site's ecological value. Utilizing recycled materials like crushed concrete for riprap or reclaimed wood for sediment barriers also helps reduce costs. Implementing simple management practices such as no-till farming can significantly decrease erosion without incurring large expenses. In urban settings, installing rain barrels or creating rain gardens can be an affordable way to manage stormwater and minimize its erosive force. The most cost-effective method will depend on local availability of materials and the specific erosion challenges of the site.
What is erosion control product?
An erosion control product is a specialized material or structure designed to prevent or minimize soil erosion caused by wind, water, or other natural forces. These products range from physical barriers, such as erosion control mats or blankets, to biodegradable items, such as straw wattles and coir logs. They are typically implemented in areas where vegetation has not been established or where natural cover is insufficient to protect the soil. The goal of these products is to reduce the speed of surface runoff, facilitate water infiltration, and provide protection for emerging seedlings, ultimately maintaining the integrity of the soil and preventing loss due to erosion.
How do you keep soil from washing away on a slope?
To keep soil from washing away on a slope, one effective method is to plant ground cover with deep root systems that will hold the soil in place. Terracing, which involves creating stepped levels on the slope, can also drastically reduce runoff and soil erosion. Additional strategies include using erosion control fabrics or mat that protect the soil surface while vegetation becomes established, and constructing retaining walls or riprap barriers to physically prevent the soil from moving. Incorporating organic matter such as mulch or compost can improve soil structure and increase its ability to absorb water, further preventing erosion. For immediate protection, sediment control devices like silt fencing or straw wattles can be installed to catch and slow the movement of sediment.
What is the best way to cover the soil from erosion?
The best way to cover and protect soil from erosion is by establishing a vegetative cover such as grass, shrubs, or other ground cover plants that can stabilize the soil with their root systems. In tandem with vegetation, mulching with organic materials like straw or wood chips can provide immediate surface protection, helping to absorb the impact of raindrops and reduce the speed of water runoff. For areas where vegetation takes time to establish, erosion control blankets, mats, or geotextiles can be applied as they offer a temporary protective layer and support plant growth. Additionally, employing earth-shaping techniques such as terracing or contouring can help reduce the velocity of water flow and enhance the soil's ability to retain water, thereby preventing erosion.
How do you stop a hill from eroding?
To stop a hill from eroding, stabilizing the slope is crucial. This can be achieved by planting a variety of deep-rooted vegetation that can hold the soil together and absorb excess water. Another method is the construction of terraces or retention walls which break up the slope and prevent water from rushing down its length. Employing erosion control products like geotextiles, erosion control blankets, or biodegradable mats can provide immediate protection while vegetation becomes established. Strategic placement of rocks or riprap can also dissipate the energy of flowing water and minimize soil displacement. It is important to integrate these measures with proper drainage systems to effectively manage water flow and reduce its erosive potential on the hill.
What is the best natural defense against erosion?
The best natural defense against erosion is a robust vegetation cover, which includes a mix of trees, shrubs, grasses, and groundcovers. The roots of these plants bind the soil together, reducing its susceptibility to wind and water forces. Additionally, the canopy created by vegetation buffers the impact of raindrops, decreasing the potential for soil displacement. For shorelines and riverbanks, mangroves and other wetland plants are extremely effective in reducing erosion by dampening the force of waves and stabilizing sediment with their complex root systems. Moreover, the practice of maintaining natural vegetation buffers around fields and waterways is a sustainable and eco-friendly approach to preserving soil integrity and preventing erosion.
Can you use landscape fabric for erosion control?
Yes, landscape fabric can be used for erosion control. It acts as a barrier to minimize soil loss while allowing water and air to penetrate, promoting healthy soil conditions. When installed properly, landscape fabric can support the soil structure on slopes and in garden beds, preventing the washing away of soil during heavy rains. It is often used in conjunction with other erosion control measures such as planting vegetation, applying mulch, or installing retaining walls for enhanced stability. The fabric is particularly effective when covered with a layer of organic material like mulch or straw, which also helps to retain soil moisture and suppress weed growth, further protecting against erosion.
What are 10 ways to reduce soil erosion?
Ten ways to reduce soil erosion include:Planting vegetation:
Trees, shrubs, grasses, and ground covers can anchor soil with their roots.
Using mulch and organic matter: Covering the soil with mulch or compost can protect it from the impact of raindrops and reduce runoff.
Building terraces: Terracing on slopes breaks up the land into flatter, more manageable sections, slowing water flow.
Constructing retaining walls: These can hold back soil on steep slopes and prevent landslides.
Implementing contour farming: Planting along the natural contours of the land reduces water flow and soil loss.
Applying geotextiles: Synthetic or natural fabrics can be used to stabilize soil, support plant growth, and filter water.
Creating windbreaks: Planting trees or shrubs to act as barriers against wind can minimize wind erosion.
Establishing riparian buffers: Vegetated areas along waterways can trap sediment and prevent stream bank erosion.
Utilizing cover crops: Growing crops during off-season periods protects the soil from erosion and improves soil health.
Practicing no-till or reduced-till farming: Minimizing soil disturbance helps maintain soil structure and reduce erosion.
These methods, individually or in combination, can effectively minimize soil erosion and preserve land fertility.
How can architecture and botany be integrated into erosion control products like geotextiles and hydromulch for sustainable land development?
Combining architectural design with botany allows for the creation of erosion control products that work with the natural environment. For example, geotextiles can be used for soil stabilization and reinforcement in construction, which, when combined with hydromulch that includes seeds selected through botanic expertise, creates a synergy that effectively prevents erosion and promotes vegetation in land development projects.
In agricultural and construction projects, how do factors like soil texture, climate, and seasonal variations influence the selection and application of erosion control measures such as silt fences, geocells, and gabions?
In both agricultural and construction projects, understanding soil texture is crucial for choosing the right erosion control solution, such as the mesh size in silt fences or the cell size in geocells. Climate factors, including the risk of corrosion from humidity or UV damage, inform the choice of materials and any necessary coatings. Seasonal changes guide the timing of installation and maintenance schedules, ensuring that solutions like gabions withstand seasonal storms and manage water flow effectively.
How does the commitment to environmental sustainability within the supply chain enhance the longevity and effectiveness of erosion control accessories, and what practices ensure the durability of these products against factors like corrosion and UV damage?
Sustainable supply chain practices enhance the effectiveness of erosion control accessories by ensuring that the materials used, such as UV-resistant polyvinyl chloride for geotextiles or corrosion-resistant coatings for steel elements in gabions, are durable and environmentally friendly. Additionally, proper maintenance and the selection of perennial plant seeds for erosion control contribute to the longevity of these products, while practices like the reuse of certain materials can bolster environmental and economic sustainability.
How can problem solving in spatial planning enhance the application of erosion control techniques in urban settings, like managing stormwater runoff on highways or in residential areas?
Problem solving in the spatial planning of urban environments is key to implementing effective erosion control techniques. For instance, strategically placed sandbags can serve as quick solutions for flood management along highways, maximizing limited space for immediate water diversion. Similarly, the use of tackifiers in hydroseeding helps to secure soil and seeds in residential areas where space is at a premium, reducing runoff and maintaining the integrity of green spaces. These problem-solving approaches, combined with the installation of dewatering bags and strategic vegetation planting, address the unique challenges of managing stormwater and preventing erosion in densely built environments.
How does the weaving technique enhance the physical strength of erosion control products like jute and nonwoven fabric geotextiles?
Weaving techniques are crucial in creating durable erosion control products. For instance, tightly woven jute fabrics and nonwoven geotextiles are designed to withstand various environmental stresses. This manufacturing process imparts the physical strength necessary for the products to prevent soil displacement and survive different seasons and temperatures, from the heat of asphalt concrete-laden highways to the moisture of a farm's field.
Can peat be considered a viable natural resource for agricultural erosion control, and what are the cost benefits compared to mechanically stabilized earth methods?
Peat, with its ability to retain water and support germination, is a valuable natural resource for agriculture-based erosion control, especially in locations with a high frequency of storms or monsoons. While mechanically stabilized earth provides a more structured solution, peat can be more cost-effective and offers a softer, organic approach suitable for farms or areas near natural fjords where environmental sensitivity is crucial.
What type of coatings are applied to erosion control products to ensure longevity and effectiveness, particularly for those used in high-traffic areas like highways or construction sites near outlet stores and houses?
Coatings on erosion control products, such as UV-resistant treatments on polyester fabrics or water-repellent layers on wood wool and hessian fabric, are applied to extend product lifetime. These coatings protect against elements such as UV rays and moisture, ensuring that the products remain effective even with the heavy wear they may experience in high-traffic areas like highways or the busy logistics environment of construction sites.
In the context of everyday life, how can the average homeowner use retail-available erosion control solutions like gabions or tackifiers for landscaping and weed control around their house and garden?
Homeowners can easily integrate erosion control solutions into their everyday gardening practices. Retail-available products like gabions can be used for aesthetic and functional landscaping, doubling as garden walls or benches, while tackifiers can be applied during seeding to enhance growth and weed control. These practices not only improve the appearance of a home's landscape but also contribute to the overall health of the environment by preserving topsoil and supporting the ecosystem.
FAQs
Your frequently asked questions answered
What is the best material to stop erosion?
The best material to stop erosion can vary depending on the specific conditions and requirements of the site in question. Organic mulches like straw and wood fiber are indeed very effective, as they not only shield the soil from the direct impact of rainfall but also facilitate the establishment of vegetation by improving soil moisture retention. For steeper slopes or areas with faster-moving water, erosion control blankets, coir logs (coconut husk), or riprap—large stones used to stabilize shorelines and stream banks—may be necessary. In addition, living plants are excellent at preventing erosion; deep-rooted grasses and shrubs can stabilize the soil and dissipate the energy of flowing water. Ultimately, the optimal choice is a combination of materials and methods tailored to the local environment, soil type, slope, and the level of erosive forces present.
What is the best erosion control?
The best erosion control strategies typically involve a combination of techniques that address the specific needs of the landscape in question. These strategies can include the use of physical barriers such as rocks, sediment control logs, and perimeter control fencing to intercept and slow down surface water flow, thereby reducing erosion potential. Vegetative measures are also pivotal, with plants, grasses, and trees acting as a natural defense to anchor the soil. Moreover, land management practices like terracing and contouring can significantly decrease erosion on slopes by altering the physical landscape to minimize runoff velocity and soil displacement. Selecting and combining these approaches based on the land's characteristics ensures the most effective protection against erosion.
What is the cheapest erosion control?
The cheapest erosion control methods are those that are cost-effective and make use of readily available materials. These often include the application of agricultural by-products such as straw, which can be used as a mulch to cover bare soil and prevent erosion. Planting fast-growing grasses or ground cover is another economical solution, as it provides quick stabilization of the soil with the additional benefit of enhancing the site's ecological value. Utilizing recycled materials like crushed concrete for riprap or reclaimed wood for sediment barriers also helps reduce costs. Implementing simple management practices such as no-till farming can significantly decrease erosion without incurring large expenses. In urban settings, installing rain barrels or creating rain gardens can be an affordable way to manage stormwater and minimize its erosive force. The most cost-effective method will depend on local availability of materials and the specific erosion challenges of the site.
What is erosion control product?
An erosion control product is a specialized material or structure designed to prevent or minimize soil erosion caused by wind, water, or other natural forces. These products range from physical barriers, such as erosion control mats or blankets, to biodegradable items, such as straw wattles and coir logs. They are typically implemented in areas where vegetation has not been established or where natural cover is insufficient to protect the soil. The goal of these products is to reduce the speed of surface runoff, facilitate water infiltration, and provide protection for emerging seedlings, ultimately maintaining the integrity of the soil and preventing loss due to erosion.
How do you keep soil from washing away on a slope?
To keep soil from washing away on a slope, one effective method is to plant ground cover with deep root systems that will hold the soil in place. Terracing, which involves creating stepped levels on the slope, can also drastically reduce runoff and soil erosion. Additional strategies include using erosion control fabrics or mat that protect the soil surface while vegetation becomes established, and constructing retaining walls or riprap barriers to physically prevent the soil from moving. Incorporating organic matter such as mulch or compost can improve soil structure and increase its ability to absorb water, further preventing erosion. For immediate protection, sediment control devices like silt fencing or straw wattles can be installed to catch and slow the movement of sediment.
What is the best way to cover the soil from erosion?
The best way to cover and protect soil from erosion is by establishing a vegetative cover such as grass, shrubs, or other ground cover plants that can stabilize the soil with their root systems. In tandem with vegetation, mulching with organic materials like straw or wood chips can provide immediate surface protection, helping to absorb the impact of raindrops and reduce the speed of water runoff. For areas where vegetation takes time to establish, erosion control blankets, mats, or geotextiles can be applied as they offer a temporary protective layer and support plant growth. Additionally, employing earth-shaping techniques such as terracing or contouring can help reduce the velocity of water flow and enhance the soil's ability to retain water, thereby preventing erosion.
How do you stop a hill from eroding?
To stop a hill from eroding, stabilizing the slope is crucial. This can be achieved by planting a variety of deep-rooted vegetation that can hold the soil together and absorb excess water. Another method is the construction of terraces or retention walls which break up the slope and prevent water from rushing down its length. Employing erosion control products like geotextiles, erosion control blankets, or biodegradable mats can provide immediate protection while vegetation becomes established. Strategic placement of rocks or riprap can also dissipate the energy of flowing water and minimize soil displacement. It is important to integrate these measures with proper drainage systems to effectively manage water flow and reduce its erosive potential on the hill.
What is the best natural defense against erosion?
The best natural defense against erosion is a robust vegetation cover, which includes a mix of trees, shrubs, grasses, and groundcovers. The roots of these plants bind the soil together, reducing its susceptibility to wind and water forces. Additionally, the canopy created by vegetation buffers the impact of raindrops, decreasing the potential for soil displacement. For shorelines and riverbanks, mangroves and other wetland plants are extremely effective in reducing erosion by dampening the force of waves and stabilizing sediment with their complex root systems. Moreover, the practice of maintaining natural vegetation buffers around fields and waterways is a sustainable and eco-friendly approach to preserving soil integrity and preventing erosion.
Can you use landscape fabric for erosion control?
Yes, landscape fabric can be used for erosion control. It acts as a barrier to minimize soil loss while allowing water and air to penetrate, promoting healthy soil conditions. When installed properly, landscape fabric can support the soil structure on slopes and in garden beds, preventing the washing away of soil during heavy rains. It is often used in conjunction with other erosion control measures such as planting vegetation, applying mulch, or installing retaining walls for enhanced stability. The fabric is particularly effective when covered with a layer of organic material like mulch or straw, which also helps to retain soil moisture and suppress weed growth, further protecting against erosion.
What are 10 ways to reduce soil erosion?
Ten ways to reduce soil erosion include:Planting vegetation:
Trees, shrubs, grasses, and ground covers can anchor soil with their roots.
Using mulch and organic matter: Covering the soil with mulch or compost can protect it from the impact of raindrops and reduce runoff.
Building terraces: Terracing on slopes breaks up the land into flatter, more manageable sections, slowing water flow.
Constructing retaining walls: These can hold back soil on steep slopes and prevent landslides.
Implementing contour farming: Planting along the natural contours of the land reduces water flow and soil loss.
Applying geotextiles: Synthetic or natural fabrics can be used to stabilize soil, support plant growth, and filter water.
Creating windbreaks: Planting trees or shrubs to act as barriers against wind can minimize wind erosion.
Establishing riparian buffers: Vegetated areas along waterways can trap sediment and prevent stream bank erosion.
Utilizing cover crops: Growing crops during off-season periods protects the soil from erosion and improves soil health.
Practicing no-till or reduced-till farming: Minimizing soil disturbance helps maintain soil structure and reduce erosion.
These methods, individually or in combination, can effectively minimize soil erosion and preserve land fertility.
How can architecture and botany be integrated into erosion control products like geotextiles and hydromulch for sustainable land development?
Combining architectural design with botany allows for the creation of erosion control products that work with the natural environment. For example, geotextiles can be used for soil stabilization and reinforcement in construction, which, when combined with hydromulch that includes seeds selected through botanic expertise, creates a synergy that effectively prevents erosion and promotes vegetation in land development projects.
In agricultural and construction projects, how do factors like soil texture, climate, and seasonal variations influence the selection and application of erosion control measures such as silt fences, geocells, and gabions?
In both agricultural and construction projects, understanding soil texture is crucial for choosing the right erosion control solution, such as the mesh size in silt fences or the cell size in geocells. Climate factors, including the risk of corrosion from humidity or UV damage, inform the choice of materials and any necessary coatings. Seasonal changes guide the timing of installation and maintenance schedules, ensuring that solutions like gabions withstand seasonal storms and manage water flow effectively.
How does the commitment to environmental sustainability within the supply chain enhance the longevity and effectiveness of erosion control accessories, and what practices ensure the durability of these products against factors like corrosion and UV damage?
Sustainable supply chain practices enhance the effectiveness of erosion control accessories by ensuring that the materials used, such as UV-resistant polyvinyl chloride for geotextiles or corrosion-resistant coatings for steel elements in gabions, are durable and environmentally friendly. Additionally, proper maintenance and the selection of perennial plant seeds for erosion control contribute to the longevity of these products, while practices like the reuse of certain materials can bolster environmental and economic sustainability.
How can problem solving in spatial planning enhance the application of erosion control techniques in urban settings, like managing stormwater runoff on highways or in residential areas?
Problem solving in the spatial planning of urban environments is key to implementing effective erosion control techniques. For instance, strategically placed sandbags can serve as quick solutions for flood management along highways, maximizing limited space for immediate water diversion. Similarly, the use of tackifiers in hydroseeding helps to secure soil and seeds in residential areas where space is at a premium, reducing runoff and maintaining the integrity of green spaces. These problem-solving approaches, combined with the installation of dewatering bags and strategic vegetation planting, address the unique challenges of managing stormwater and preventing erosion in densely built environments.
How does the weaving technique enhance the physical strength of erosion control products like jute and nonwoven fabric geotextiles?
Weaving techniques are crucial in creating durable erosion control products. For instance, tightly woven jute fabrics and nonwoven geotextiles are designed to withstand various environmental stresses. This manufacturing process imparts the physical strength necessary for the products to prevent soil displacement and survive different seasons and temperatures, from the heat of asphalt concrete-laden highways to the moisture of a farm's field.
Can peat be considered a viable natural resource for agricultural erosion control, and what are the cost benefits compared to mechanically stabilized earth methods?
Peat, with its ability to retain water and support germination, is a valuable natural resource for agriculture-based erosion control, especially in locations with a high frequency of storms or monsoons. While mechanically stabilized earth provides a more structured solution, peat can be more cost-effective and offers a softer, organic approach suitable for farms or areas near natural fjords where environmental sensitivity is crucial.
What type of coatings are applied to erosion control products to ensure longevity and effectiveness, particularly for those used in high-traffic areas like highways or construction sites near outlet stores and houses?
Coatings on erosion control products, such as UV-resistant treatments on polyester fabrics or water-repellent layers on wood wool and hessian fabric, are applied to extend product lifetime. These coatings protect against elements such as UV rays and moisture, ensuring that the products remain effective even with the heavy wear they may experience in high-traffic areas like highways or the busy logistics environment of construction sites.
In the context of everyday life, how can the average homeowner use retail-available erosion control solutions like gabions or tackifiers for landscaping and weed control around their house and garden?
Homeowners can easily integrate erosion control solutions into their everyday gardening practices. Retail-available products like gabions can be used for aesthetic and functional landscaping, doubling as garden walls or benches, while tackifiers can be applied during seeding to enhance growth and weed control. These practices not only improve the appearance of a home's landscape but also contribute to the overall health of the environment by preserving topsoil and supporting the ecosystem.















Facebook